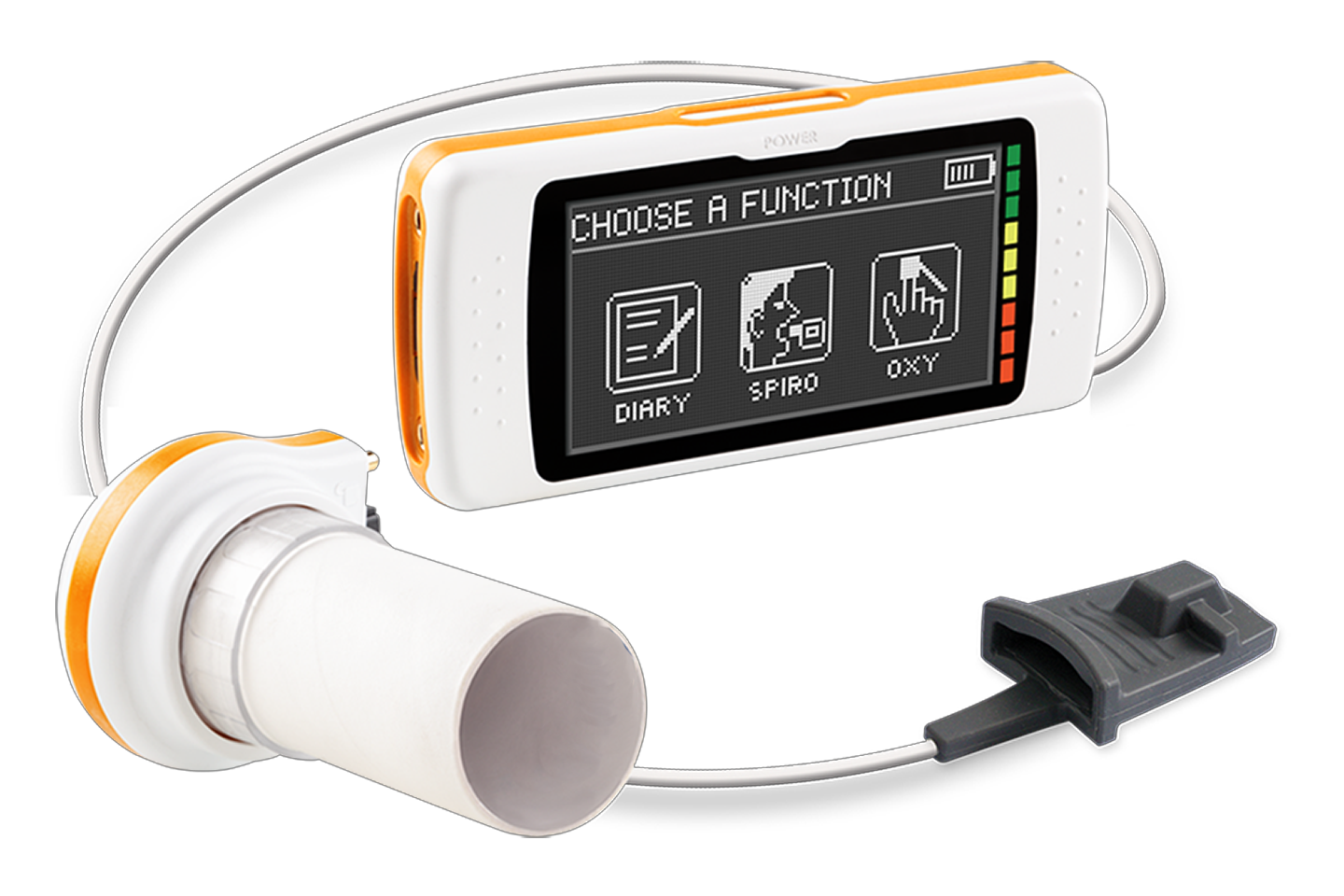
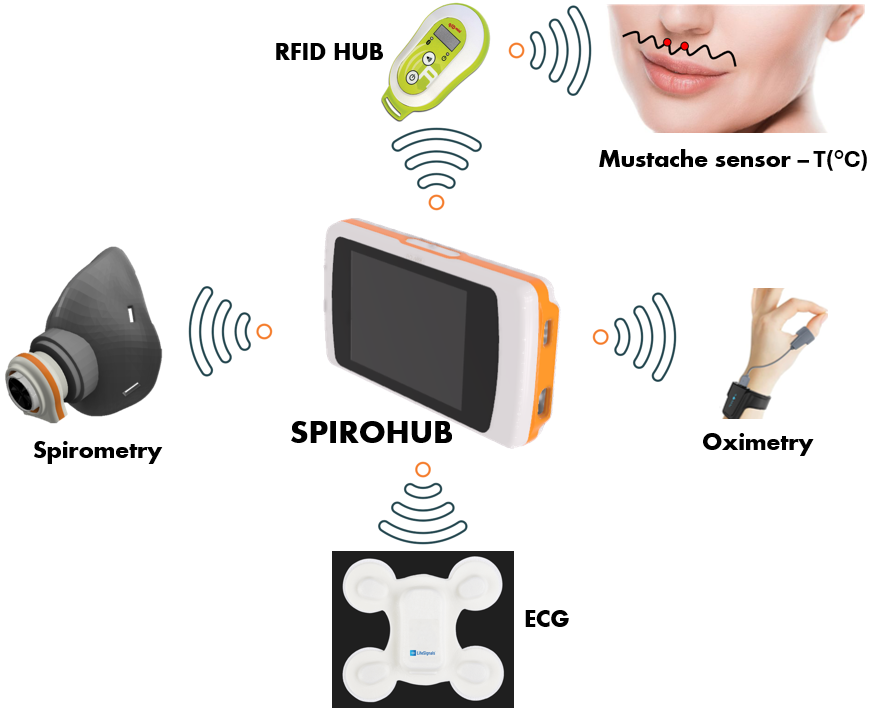
SPIROHUB
Development of an innovative E-Health device called SPIROHUB, for monitoring respiratory rate and vital parameters based on non-invasive wireless sensors and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies for data analysis for medical diagnostics
Valore totale del progetto: 291.714,14 € di cui 291.714,14 € a titolo di sostegno finanziario ricevuto dalla Regione Lazio.
ORIGINE DEI FONDI: FESR Fondo Europeo di Sviluppo Regionale Programma Operativo regionale del Lazio
|
|
    Project
carried out with the contribution of:
MIR - Medical
International Research S.p.a. e
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile ed
Ingegneria Infromatica (DICII)
dell'Università degli Studi di Roma Tor
vergata.
Programma FESR Lazio 2021-2027 Avviso Riposizionamento Competitivo RSI Ambito 1 “Scienze della Vita”. |
| TEAM UNI TV Prof. Gaetano MARROCCO Prof.ssa Cecilia OCCHIUZZI Prof. Fabio PLACIDI Eng. Federica NACCARATA Eng. Francesca M. C. NANNI Team Leader: Eng. Andriano MENCARINI Hardware Senior Designer: Marco PENNACCHIETTI |
 |
COLLABORATIONS

|
 |
 |
 |
Background
The project addresses the needs encountered in the medical field when measuring vital parameters in non-collaborative patients over extended periods (hours or even days). In many cases, monitoring various parameters such as respiratory rate, blood oxygen saturation, heart rate, and sweat fluid quantity/quality is necessary, particularly in situations where patient cooperation is not feasible, such as during sleep studies, coma, neonatal care, or during physical activities like sports medicine.
Among various applications, the primary focus is on
polysomnography, the gold standard for diagnosing
sleep-related breathing disorders like sleep apnea and
snoring. These disorders affect approximately one in
four adults in Italy, according to recent data from
the Italian Association of Sleep Medicine (AIMS).
Polysomnography objectively studies sleep by recording
physiological variables during different sleep stages
(REM and non-REM). However, measuring and monitoring
respiratory rate in this context is often challenging
due to sensor invasiveness and the cumbersome wiring
connections to the receiver. The new SPIROHUB device
with wireless sensors resolves these issues, making
measurements more accessible and reliable, greatly
benefiting diagnostics. Additionally, it facilitates
diagnosis for medical professionals by employing
real-time sensor data processing using AI algorithms
trained to recognize diagnostic patterns.
Aims
The goal of the project is to develop an innovative electromedical device called SPIROHUB capable of:
- Collecting data on patients' vital parameters transmitted by various non-invasive, low-power sensors capable of operating wirelessly and communicating via wireless communication for extended periods.
- Allowing for the visualization and management of collected data.
- Enabling the processing and analysis of vital parameter trends through innovative Artificial Intelligence algorithms, facilitating rapid diagnosis.

.png)
.png)
.png)

C66 Mobile Computer (Android 11)


20 February 2024
Kick-off Meeting



