MILESTONES
Kick-off: 15 April 2021
End date: 15 April 2024

Valore totale del progetto: 146.020,05 € di cui 146.020,05 € a titolo di sostegno finanziario ricevuto dalla Regione Lazio.
ORIGINE DEI FONDI: FESR Fondo Europeo di Sviluppo Regionale - Programma Operativo regionale del Lazio - Programmazione 2014-2020. Avviso Pubblico: "Progetti di Gruppi di Ricerca 2020".
   |
   Progetto
realizzato con il contributo di:
Regione Lazio, Lazio Innova. POR FESR Lazio 2014-2020. Avviso pubblico "Progetti di Gruppi di Ricerca 2020". |
| TEAM Prof.ssa Fabiana ARDUINI Prof.ssa Cecilia OCCHIUZZI Dott.ssa Viviana SCOGNAMIGLIO Dott.ssa Mattea C. CASTROVILLI Dott. Armando ORLANDI Prof. Pierpaolo LORETI |
|
COLLABORATIONS
 |
|
 |
Background
English
The vast majority of oral anticancer
treatments, administered at home, and intravenous
infusions in medical oncology units, can lead to a
limitation of physiological marrow, liver, and renal
functions. Therefore, periodic determination of the
blood count (hemoglobin, platelet count, and leukocyte
formula) and plasma electrolytes (potassium, sodium,
calcium, and magnesium) is mandatory for proper
monitoring of drug toxicity and to identify the most
appropriate dosage for each individual patient.
In recent years, the introduction of oral targeted
molecular drugs in the treatment of hormone-sensitive
metastatic breast carcinoma, such as cyclin-dependent
kinase 4/6 inhibitors (CDK 4/6i), proteins that modulate
the cell division cycle, have revolutionized the
treatment of one of the most common oncological
diseases. With the introduction of these drugs and a
significant improvement in patient survival, there has
been a reduction in hospitalization, but also the
simultaneous need for careful monitoring of blood
dyscrasia and electrolytes, especially in the first 4-6
months of treatment, in order to monitor the specific
toxicity of these drugs and identify the correct dosage.
CDK 4/6 inhibitors (ribociclib, palbociclib, and
abemaciclib) not only exhibit significant anticancer
activity but also specifically inhibit marrow precursors
causing neutropenia and cardiotoxicity (exclusively
associated with ribociclib) with an increase in the QT
interval of the electrocardiogram which can lead to
alterations, even anecdotally fatal, in cardiac rhythm.
This specific spectrum of toxicity necessitates
monitoring of the blood count, leukocyte formula, and
plasma electrolytes, whose homeostasis is essential for
proper myocardial contraction.
La quasi totalità dei trattamenti
antineoplastici orali, somministrati a domicilio, ed
endovenosi, infusi nelle unità assistenziali di
oncologia medica, possono determinare una limitazione
delle fisiologiche funzionalità midollare, epatica e
renale. A fronte di ciò la determinazione periodica
dell’emocromo (emoglobina, conta piastrinica e formula
leucocitaria) e degli elettroliti plasmatici (potassio,
sodio, calcio, e magnesio) risulta essere mandatoria al
fine di un corretto monitoraggio della tossicità dei
farmaci e di individuarne la più adatta posologia per
ogni singolo paziente.
Negli ultimi anni l’introduzione di farmaci orali a
bersaglio molecolare nel trattamento del carcinoma della
mammella metastatico ormono-sensibile, come gli
inibitori delle cicline chinasidipendenti 4/6 (CDK 4/6i)
proteine modulatrici del ciclo di divisione cellulare,
hanno rivoluzionato il trattamento di una delle
patologie oncologiche più frequenti. A fronte
dell’introduzione di tali farmaci con un significativo
miglioramento della sopravvivenza delle pazienti, si è
assistito ad una ridotta ospedalizzazione, ma alla
contestuale necessità di un attento monitoraggio della
crasi ematica e degli elettroliti, principalmente nei
primi 4-6 mesi di trattamento al fine di monitorare la
tossicità specifica di questi farmaci ed individuarne il
più corretto dosaggio.
I CDK 4/6i (ribociclib, palbociclib e abemaciclib)
presentano, oltre ad una significativa attività
antineoplastica, una specifica inibizione dei precursori
midollari causando neutropenia e tossicità cardiologica
(legata esclusivamente al ribociclib) con incremento del
tratto QT dell’elettrocardiogramma che può determinare
alterazioni, anche aneddoticamente fatali, del ritmo
cardiaco. Questo spettro specifico di tossicità rende
necessario il monitoraggio dell’emocromo, della formula
leucocitaria e degli elettroliti plasmatici, la cui
omeostasi è essenziale per la corretta contrazione
miocardica.
Goals (Obbiettivi)
English
Development of
- Paper-based biosensor platform for blood count and electrolytes.
- NFC potentiostat.
- Digital Health App and Cloud.
- Secure data sharing/transmission system.
- Improved quality of life.
- Time savings.
- Cost-effectiveness.
- Quality of service.
Italiano
Sviluppo di:
- Piattaforma biosensoristica su carta per emocromo ed elettroliti.
- Potenziostato NFC.
- App e Cloud per Sanità Digitale.
- Sistema di condivisione/trasmissione sicura dei dati.
- Qualità della vita.
- Risparmio di tempo.
- Economicità.
- Qualità del servizio.

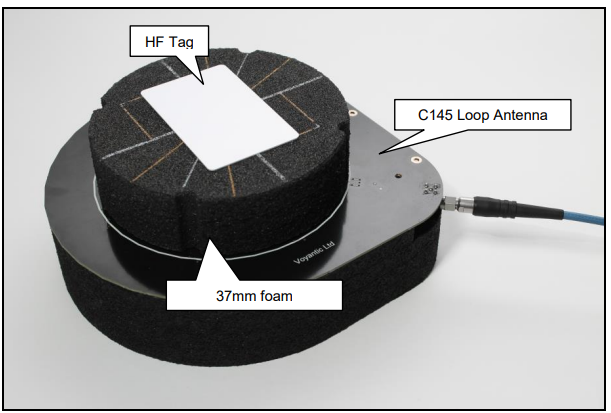
C66 Mobile Computer (Android 11)


5 Luglio 2021
Kick-off Meeting
Keynote - Conferenza IEEE RFID TA
Prof.ssa F. Arduini
Workshop - Villa Celimontana, Roma
Prof.ssa Occhiuzzi

The workshop is dedicated to the presentation of the research activity carried out within the E-CROME project: Development of biosensors with wireless RFID-NFC interface for telemedicine, in the context of home care for oncological and terminal patients, in line with the regional ecosystem of innovation (Digital Health) and the theatics proper to Life Sciences (biosensors, telemedicine) and Security (Cyber security and privacy) funded by POR FESR Lazio 2014 - 2020, Public Notice "Projects of Research Groups 2020", subject to the findings of the preliminary investigation carried out by Lazio Innova S.p.A.
L. Fiore, V. Mazzaracchio, A. Serani, G. Fabiani, L. Fabiani, G. Volpe, D. Moscone, G. M. Bianco, C. Occhiuzzi, G. Marrocco, F. Arduini, Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical (2023)

E. Raso, G. M. Bianco, L. Bracciale, G. Marrocco, C. Occhiuzzi, and P. Loreti, Sensors MDPI (2022)
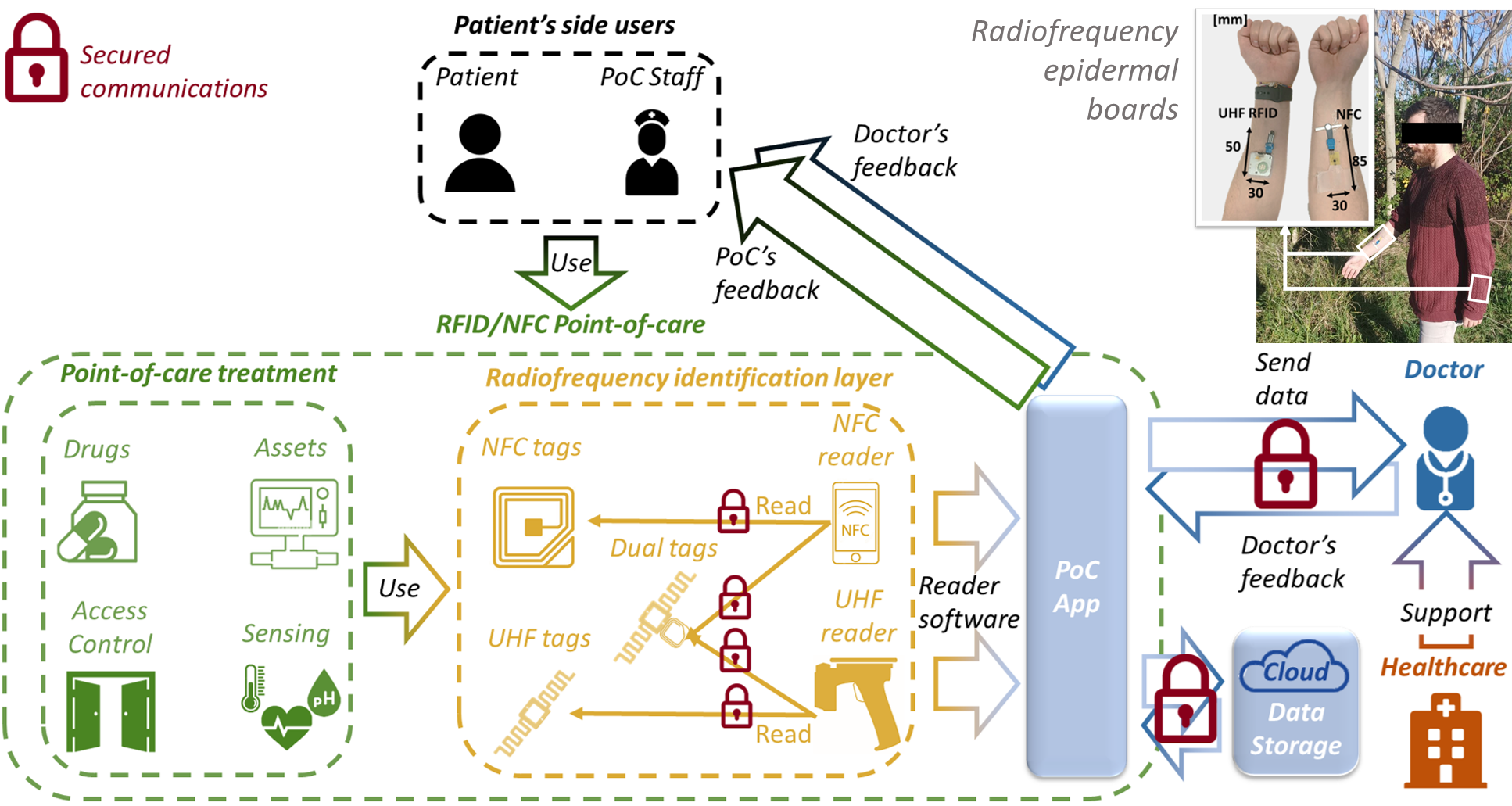
World population and life expectancy have increased steadily in recent years, raising issues regarding access to medical treatments and related expenses. Through last-generation medical sensors, NFC (Near Field Communication) and radio frequency identification (RFID) technologies can enable healthcare internet of things (H-IoT) systems to improve the quality of care while reducing costs. Moreover, the adoption of point-of-care (PoC) testing, performed whenever care is needed to return prompt feedback to the patient, can generate great synergy with NFC/RFID H-IoT systems. However, medical data are extremely sensitive and require careful management and storage to protect patients from malicious actors, so secure system architectures must be conceived for real scenarios. Existing studies do not analyze the security of raw data from the radiofrequency link to cloud-based sharing. Therefore, two novel cloud-based system architectures for data collected from NFC/RFID medical sensors are proposed in this paper. Privacy during data collection is ensured using a set of classical countermeasures selected based on the scientific literature. Then, data can be shared with the medical team using one of two architectures: in the first one, the medical system manages all data accesses, whereas in the second one, the patient defines the access policies. Comprehensive analysis of the H-IoT system can be useful for fostering research on the security of wearable wireless sensors. Moreover, the proposed architectures can be implemented for deploying and testing NFC/RFID-based healthcare applications, such as, for instance, domestic PoCs.
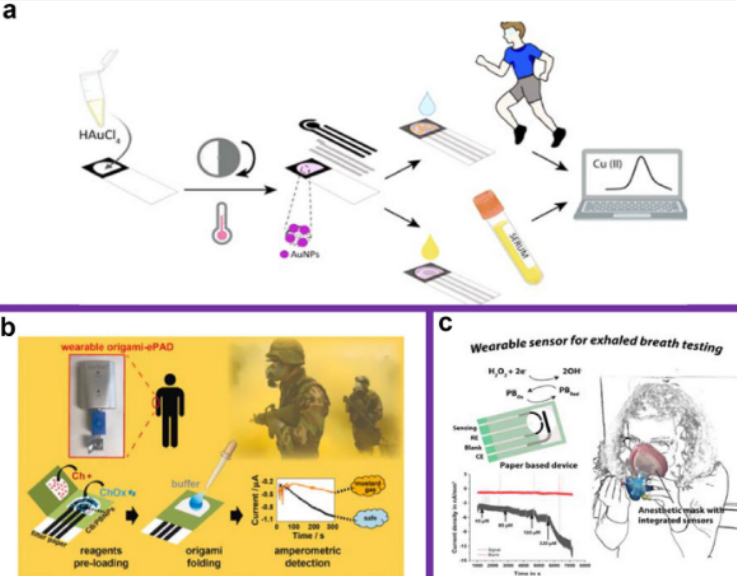
F. Arduini, Current Opinion in Electrochemistry (2022): 101090.

N. Colozza, V. Caratelli, D. Moscone F. Arduini, Biosensors 11.9 (2021):328.


G. M. Bianco, V. Mazzaracchio, L. Fiore, F. Arduini, G. Marrocco and C. Occhiuzzi, presented at IEEE SENSORS 2024, Oct. 20-23, Kobe, Japan, 2024
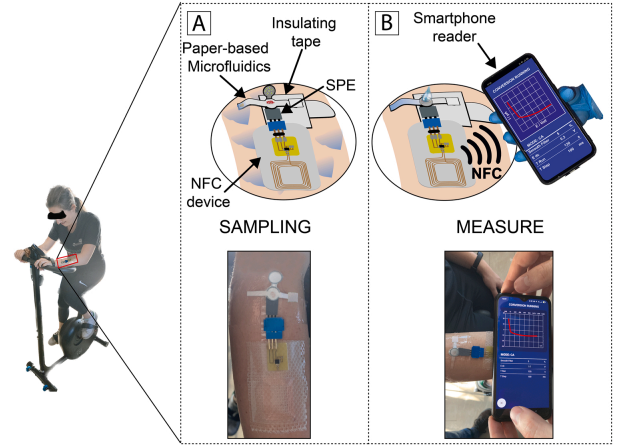
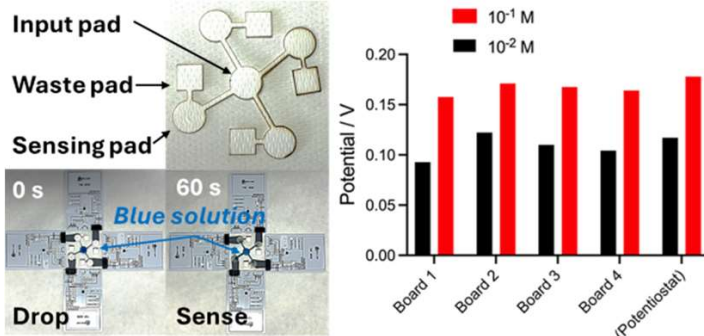
Electrochemical analysis systems are increasingly important for applications like Point-of-Care diagnostics and Lab-on-Package sensing. Herein, we propose a system composed of four passive NFC (Near Field Communication) microchips capable of performing open circuit potentiometry through interactions with commercial smartphones. The multi-chip NFC system can be used to quantify four chemical quantities within a unique liquid sample thanks to a microfluidic circuit which feeds four ad-hoc screen-printed electrodes. In this contribution, preliminary calibration on four analytes is reported. The four target quantities considered in this paper are sodium, potassium, calcium, and pH. The sensing matrix will be human blood and fluids derived from food spoilage Thanks to further implementation with microfluidic channels currently under development, the NFC chemical analyses can facilitate domestic monitoring of patients and rapid, on-site test of pieces of food to check food quality and prevent foodborne illnesses.
G. M. Bianco, V. Mazzaracchio, L. Fiore, F. Arduini, G. Marrocco, and C. Occhiuzzi, 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and ITNC-USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (AP-S/URSI 2024)
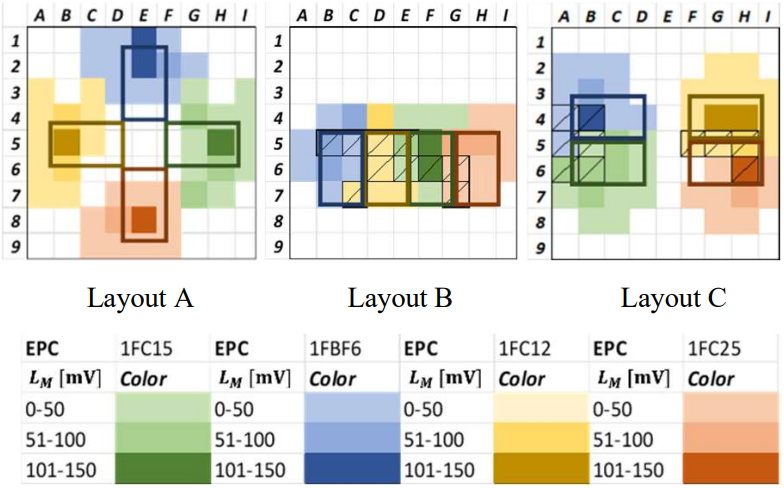
Fast, on-site chemical sensing can be a powerful tool for many applications, ranging from point-of-care analyses to food quality checks. NFC (Near Field Communications) devices capable of chemical sensing have recently become available. However, they are still limited to sensing a single chemical species at a time, whereas usually, an array of species should be quantified during the same analysis. Multi-chip NFC devices are still unavailable for chemical sensing, and the use of microfluidics with delay lines is also necessary for the correct delivery of liquid samples. Accordingly, this contribution explores the layout design of the first multi-chip NFC system integrated with microfluidics for electrochemical sensing using multiple boards simultaneously. The most functional arrangement of the responders is experimentally selected based on their read areas, the quality of the NFC communication, and the microfluidic characteristics. Lastly, a four-channel microfluidic system is integrated with the best board placement and validated by quantification of sodium in standard solution.
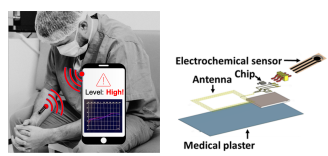
A. B. Barba, G. M. Bianco, L. Fiore, F. Arduini, G. Marrocco and C. Occhiuzzi, 2022 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS)
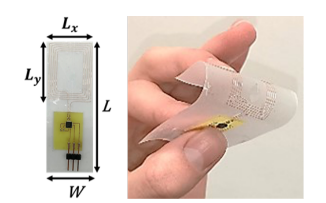
Flexible and epidermal sensing devices are becoming vital to enable precision medicine and telemonitoring systems. The NFC (Near Field Communication) protocol is also becoming increasingly important for this application since it is embedded in most smartphones that can be used as pervasive and lowcost readers. Furthermore, the responder can be passive and can harvest enough power to perform electromagnetic sensing. Finally, the NFC coils are robust to bending and to the human body’s presence. This contribution details the design of a new flexible device, including an electrochemical sensor communicating through the NFC protocol. A spiral NFC antenna is designed, and a manufactured prototype is experimentally tested to quantify the robustness to the inter-wearer variability and the bending. Lastly, the sensory data retrieval is validated by comparison with a portable potentiostat. The realized sensor can be comfortably worn and be easily read by smartphones independently from the wearer and from the point of application and could be used in future for estimating the user’s psycho-physical health by analyzing the body’s sweat.
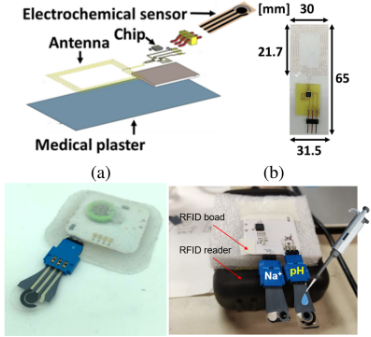
G. M. Bianco, E. Raso, L. Fiore, A. Riente, A. B. Barba, C. Miozzi, L. Bracciale, F. Arduini, P. Loreti, G. Marrocco and C. Occhiuzzi, 2022 IEEE International Conference on RFID Technology and Applications (RFID-TA)
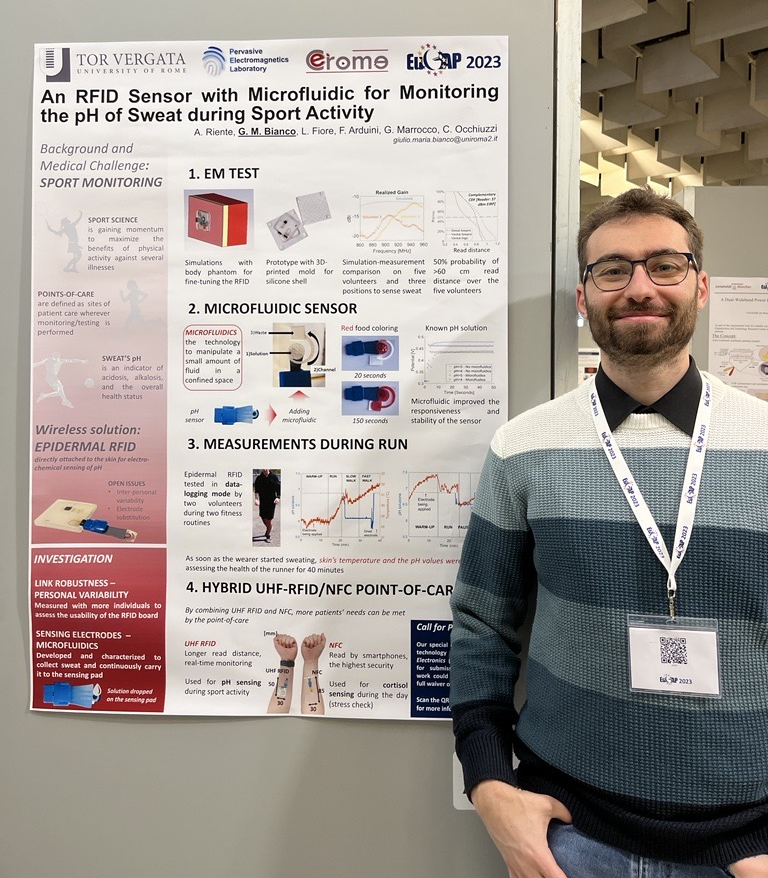

A. Riente, G. M. Bianco, L. Fiore, F. Arduini, G. Marrocco and C. Occhiuzzi, 17th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP2023)

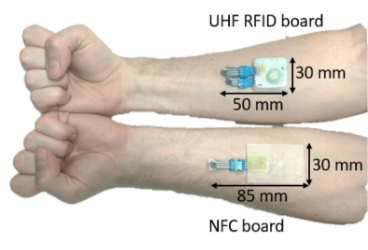
G. M. Bianco, E. Raso, L. Fiore, A. Riente, A. B. Barba, C. Miozzi, L. Bracciale, F. Arduini, P. Loreti, G. Marrocco and C. Occhiuzzi, "Towards a Hybrid UHF RFID and NFC Platform for the Security of Medical Data from a Point of Care"
